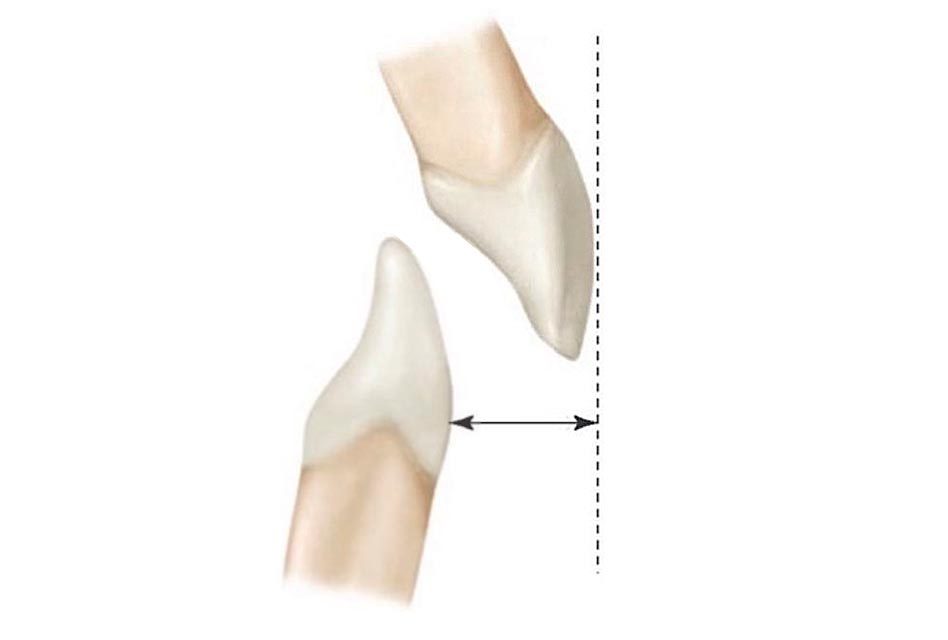
Overjet refers to the vertical distance between the maxillary central incisors and the mandibular central incisors. It is measured in millimeters between the incisal edges. Normal overjet is 1 to 2 mm. If the number is high, there can be retrognathia of the mandible, meaning that the lower jaw is placed more towards the back, or prognatia of the maxilla, where the upper jaw is placed towards the front. If the overjet is negative, then there is anterior crossbite, which means that the lower incisors are in front of upper incisors.
References
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (www.wikipedia.org).
- Medical dictionary by Farlex (www.thefreedictionary.com).
The information above should be used as a reference only. Any medical decision should not be taken before consulting a health care professional.
The masculine gender may have been more used in the article, but without prejudice, to make reading easier.
Category dental problems
- Abfraction
- Abrasion
- Ankylosis
- Anodontia
- Attrition
- Broken fillings
- Bruxism (Teeth Grinding)
- Cavity (tooth decay)
- Cold sore (herpes labialis)
- Dental abscess
- Dental plaque
- Denture Irritations and Infections
- Denture stomatitis (prosthetic stomatitis)
- Dry socket
- Erosion
- Fluorosis (dental)
- Gingival hyperplasia
- Gingival pocket
- Gingivitis
- Gum Disease (Periodontal Disease)
- Gum recession
- Halitosis (Bad Breath)
- Hyperdontia (supernumerary teeth)
- Hypocalcification
- Hypodontia
- Impacted tooth (tooth impaction)
- Leukoplakia
- Lichen planus
- Malocclusion (Misaligned Teeth)
- Microdontia
- Micrognathia (micrognathism)
- Mucocele
- Oligodontia
- Oral cancers
- Oral candidiasis
- Overbite
- Overjet
- Pericoronitis
- Periodontal pocket
- Periodontitis
- Prognathia (prognatism)
- Resorption
- Retrognathia (retrognatism)
- Sleep apnea
- Tartar (Calculus)
- TMD (Pain and Cracking of the Jaw)
- Tooth Discolouration
- Tooth sensitivity (sensitive teeth)
- Torus
- Trismus
- Ulcers and canker sores
- Xerostomia (Dry Mouth)