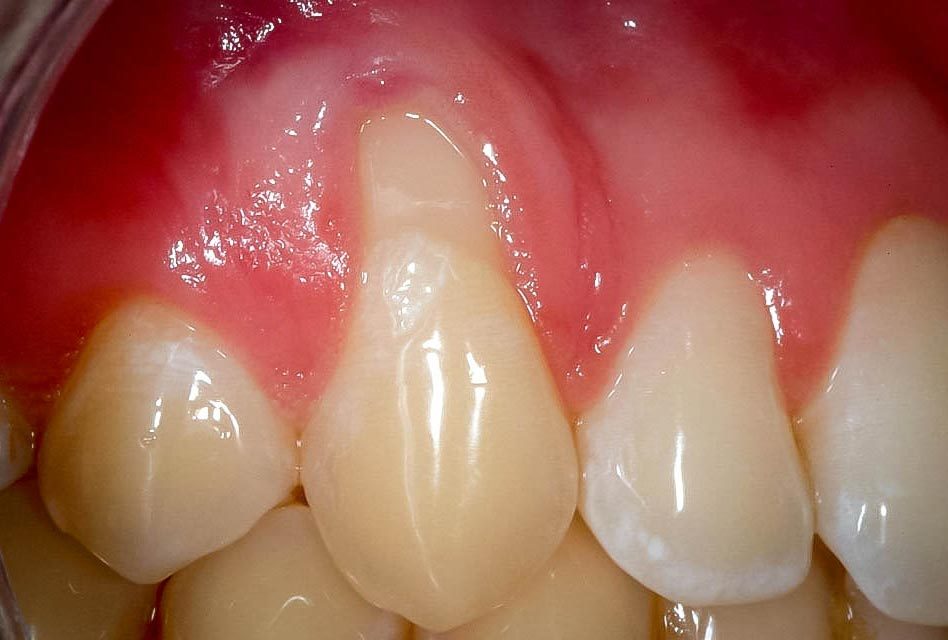
Gum recession (or periodontal recession) refers to the loss of the gum at the collar of teeth by exposing their roots. This exposure is made by retraction of the gingival tissue around the natural crowns of teeth.
When receding gums expose roots, teeth look longer because there is less gum covering them. If on top of the loss of gum there is also loss of alveolar bone, the recession is therefore referred to a periodontal recession, which is a consequence of periodontitis.
Symptoms
The recession of gums is a very slow process that takes years to develop. A person does not notice its evolution day after day until some symptoms appear:
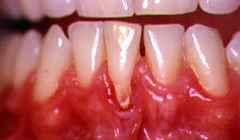 tooth sensitivity, where teeth become sensitive to cold, hot as well as to spicy, sour or sweet foods;
tooth sensitivity, where teeth become sensitive to cold, hot as well as to spicy, sour or sweet foods;- teeth appear longer than normal, because gum recession exposes roots;
- the line between a tooth and its root becomes visible, and you can even feel it with the tongue or finger;
- there is also a slight colour difference on the collar of a tooth because the enamel and dentin of the root have two different colours;
- dark triangles, or spaces appear between the teeth near the gums;
- if on top of gum recession a person is suffering from gingivitis or periodontitis, there may be redness, swelling or bleeding of the gums.
Causes
For gum recession to develop, there may be a predisposing factor, which can be then complicated by a provoking factor.
Predisposing factors:
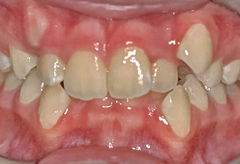 a thin gingiva (thin gums) that is lacking strength with little keratinized tissue;
a thin gingiva (thin gums) that is lacking strength with little keratinized tissue;- misaligned teeth which might be related to less bone or gums that support those teeth;
- a nearby fraenum that could pull on the gums; a fraenum is a fold of tissue that connects the gums to the lips, or the tongue to the gums, and that limits their movement.
Provoking factors:
 traumatic brushing; you must avoid hard bristled toothbrushes, even medium is too traumatic; use only a soft toothbrush and you must also not rub too hard when brushing your teeth;
traumatic brushing; you must avoid hard bristled toothbrushes, even medium is too traumatic; use only a soft toothbrush and you must also not rub too hard when brushing your teeth;- poor oral hygiene where there are deposits of plaque and tartar around the gums which can become receded with time;
- bruxism; trauma resulting from teeth grinding can affect the attachment of the gums to the teeth;
- chewing tobacco; the action of chewing tobacco weakens the attachment of gums;
- periodontitis; when gum disease affects alveolar bone that supports the teeth, the gum that covers it also becomes weakened and if it shrinks down, it is therefore referred to as periodontal recession;
- bulimia; repetitive vomiting is a type of trauma to the gums;
- lip piercing or piercing of another part inside the mouth, especially if the jewellery is metallic;
- scurvy; a disease caused by vitamin C deficiency;
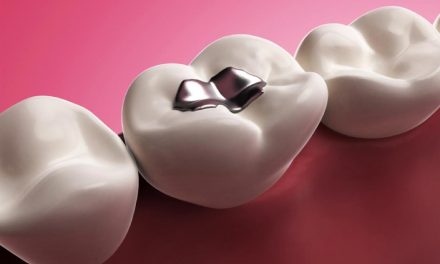
- fillings or other dental restorations that are poorly-adapted;
- excessive forces of an orthodontic treatment.
Treatments
 The first thing to do when you suffer from gum recession is to eliminate provoking factors as much as possible. You can start by improving your dental hygiene methods by brushing on a regular basis, by flossing, and by having regular dental cleanings at a dentist’s office.
The first thing to do when you suffer from gum recession is to eliminate provoking factors as much as possible. You can start by improving your dental hygiene methods by brushing on a regular basis, by flossing, and by having regular dental cleanings at a dentist’s office.
If the brushing method is too traumatic for the gum, you must modify it. A toothbrush with soft or extra-soft bristles is recommended. Gums should be cleaned gently with the toothbrush without forcing too hard.
If you are suffering from periodontal disease (periodontitis), the disease should be treated by curettage or by other treatments depending on the severity. If bruxism is causing the recession, you must reduce the grinding. If tooth grinding occurs during daytime, you can be conscious about it and avoid putting your teeth in contact with each other. But if grinding occurs while you are sleeping, a bite splint fabricated by your dentist should be worn at night.
When these factors are taken into care, the progress of gum recession should be evaluated. If it’s located in an aesthetic region, or if it compromises the tooth’s health, a gingival graft is therefore indicated.
A gum graft is a procedure that is done under local anaesthesia (the patient remains conscious) and it involves taking a piece of gum from the palate, which will be sutured on the tooth whose root is exposed. Sometimes it is possible to use a piece of human skin donor, treated and disinfected, as a graft rather than taking a piece of the palate.
References
- Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (www.wikipedia.org).
- What to do for receding gums (Khow Thy Health).
The information above should be used as a reference only. Any medical decision should not be taken before consulting a health care professional.
The masculine gender may have been more used in the article, but without prejudice, to make reading easier.
Category dental problems
- Abfraction
- Abrasion
- Ankylosis
- Anodontia
- Attrition
- Broken fillings
- Bruxism (Teeth Grinding)
- Cavity (tooth decay)
- Cold sore (herpes labialis)
- Dental abscess
- Dental plaque
- Denture Irritations and Infections
- Denture stomatitis (prosthetic stomatitis)
- Dry socket
- Erosion
- Fluorosis (dental)
- Gingival hyperplasia
- Gingival pocket
- Gingivitis
- Gum Disease (Periodontal Disease)
- Gum recession
- Halitosis (Bad Breath)
- Hyperdontia (supernumerary teeth)
- Hypocalcification
- Hypodontia
- Impacted tooth (tooth impaction)
- Leukoplakia
- Lichen planus
- Malocclusion (Misaligned Teeth)
- Microdontia
- Micrognathia (micrognathism)
- Mucocele
- Oligodontia
- Oral cancers
- Oral candidiasis
- Overbite
- Overjet
- Pericoronitis
- Periodontal pocket
- Periodontitis
- Prognathia (prognatism)
- Resorption
- Retrognathia (retrognatism)
- Sleep apnea
- Tartar (Calculus)
- TMD (Pain and Cracking of the Jaw)
- Tooth Discolouration
- Tooth sensitivity (sensitive teeth)
- Torus
- Trismus
- Ulcers and canker sores
- Xerostomia (Dry Mouth)