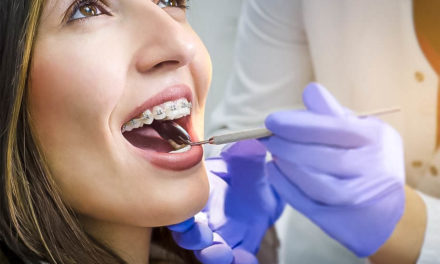
A dentist is a health professional trained and licenced to practice dentistry. The work of a dentist involves diagnosing, preventing and treating diseases, injuries and malformations of the teeth, the gums and the jaws. A dentist mainly takes care of repairing damaged teeth, extracting the ones that are too destroyed, and replacing them with prosthetic options.
History
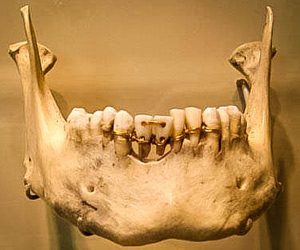 The first evidence of work done on human teeth dates back to around 7000 BC in a valley that is located in what is Pakistan today. Researchers found skeletons whose teeth had holes in them cut perfectly, probably to remove cavities.
The first evidence of work done on human teeth dates back to around 7000 BC in a valley that is located in what is Pakistan today. Researchers found skeletons whose teeth had holes in them cut perfectly, probably to remove cavities.
Centuries later, humans were aware of the existence of dental caries and thought that it was caused by “tooth worms”. This belief lasted very long, even at the age of the renaissance in Europe.
Around 500 BC, the Phoenicians had developed a few techniques of dental prosthesis. Among others they would bind teeth that were moving too much (because of periodontitis) to other solid teeth with a gold wire. This technique prevented the mobile teeth from falling.
 Greek scholars like Hippocrates and Aristotle initiated the modern knowledge on a number of dental topics like tooth eruption, the treatment of tooth decay, gum disease, and the extraction of teeth using forceps.
Greek scholars like Hippocrates and Aristotle initiated the modern knowledge on a number of dental topics like tooth eruption, the treatment of tooth decay, gum disease, and the extraction of teeth using forceps.
The profession of dentist did not exist as such. It was mostly doctors and barbers who treated teeth or extracted them. In the seventeenth century Pierre Fauchard developed modern dentistry by introducing sophisticated instruments to treat teeth with fillings. He also studied the relationship between sugar and tooth decay. After Fauchard, the profession of dentist grew more with the techniques and knowledge that we have today.
Schooling
Before studying dentistry, students must have earned a pre-university degree with extensive knowledge in biology, chemistry, organic chemistry, physics, and mathematics. In several countries, a dentist is a qualified health professional to practice dentistry after obtaining a university degree in either Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) ou in Docteur en Médecine Dentaire (DMD).
Like all fields, medicine and dentistry techniques are constantly evolving. Dentists must update their knowledge throughout their careers as new techniques provide many benefits to their patients.
Responsibilities
 On top of examining teeth, taking x-rays and finding a diagnosis, a dentist can perform several treatments to his or her patients:
On top of examining teeth, taking x-rays and finding a diagnosis, a dentist can perform several treatments to his or her patients:
- Restore teeth with (fillings, crowns and bridges.
- Replace missing teeth with dentures, bridges or implants.
- Save teeth with root canal therapy.
- Treat gum disease.
- Straighten miss-aligned teeth with braces (orthodontics).
- Extract the teeth that can not be saved.
Dentists can also prescribe medications such as antibiotics, analgesics (pain killers) and sedatives.
The dentist’s team normally includes the dental hygienist, the dental assistant and the secretary. There are also other professions that are complementary in dentistry, and they include denturists who are trained to prepare dentures, and laboratory technicians who create crowns, bridges and dentures.
Specialties
A specialist in dentistry is a person who has been trained as a dentist but went on to specialize in a particular discipline. In most countries, we find the following fields of dental specialists (the masculine gender is used here although dentists and specialists can all be equally men and women):
- A public health dentist studies dental epidemiology (cavity, gingivitis, etc.) and social health policies.
- An endodontist is a specialist of root canal treatments and the analysis of the diseases of the dental pulp.
- An oral and maxillofacial pathologist (oral medicine) specializes in the study, diagnosis and sometimes treatment of diseases and physiological problems, which occur or have signs in the mouth and jaws.
- An oral and maxillofacial radiologist is dedicated to the study and radiological interpretation of diseases of the mouth and jaws.
- An oral and maxillofacial surgeon (not to be confused with a dental surgeon) specializes in more difficult surgical procedures such as complicated extractions, dental implants, as well as jaw surgery, which also include the correction of facial birth defects.
- An orthodontist is dedicated to straightening teeth and aligning jaws orthopedically.
- A periodontist specializes in the surgical or non-surgical treatment of gum disease (gingivitis and periodontitis), and the placement and maintenance of dental implants.
- A paediatric dentist is the specialist that takes care of oral health for children.
- A prosthodontist restores teeth with prosthesis (dentures, veneers, crowns, bridges, or crowns on implants).
There are also specialties that are not yet recognized or almost recognized in the dental community, such as implantology or geriatric dentistry.
References
- 9,000-Year-Old Dentistry (Wired).
- Interesting Phoenician Info (Phoenician Language).
- Dentistry (Wikipedia).
- Dentist (Wikipedia).
The information above should be used as a reference only. Any medical decision should not be taken before consulting a health care professional.
The masculine gender may have been more used in the article, but without prejudice, to make reading easier.